
The 2FA, or two-factor authentication, is a security measure that adds an extra layer of protection to your online accounts. It requires users to provide two different types of identification factors to verify their identity. These factors typically fall into three categories:
Something you know: This includes passwords, PINs, or answers to security questions.
Something you have: This involves possession of a physical item, such as a mobile device, security token, or smart card.
Something you are: This refers to biometric data, such as fingerprints, iris scans, or facial recognition.
The main advantage of 2FA is that it significantly enhances the security of your online accounts by making it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Here are some key benefits:
Increased Security: 2FA adds an additional layer of protection beyond just a password. Even if someone discovers or guesses your password, they would still need the second factor to successfully authenticate.
Mitigates Password Vulnerabilities: Many security breaches occur due to weak or stolen passwords. With 2FA, even if your password is compromised, the attacker would still need the second factor to gain access.
Phishing Resistance: Phishing attacks involve tricking users into revealing their login credentials on fake websites. 2FA can help prevent these attacks since the attacker would need the second factor, which they typically don’t have.
Convenience: While it may seem like an extra step, 2FA provides added peace of mind. With the availability of various authentication methods, such as SMS codes, authenticator apps, or biometric scans, it has become relatively easy to implement and use.
Industry Best Practice: 2FA is widely recommended by cybersecurity experts and organizations as a standard security measure. Many online platforms, including email services, social media, banking, and cloud storage providers, encourage or require the use of 2FA to safeguard user accounts.
It is important to note that while 2FA significantly enhances security, it is not foolproof. There can still be potential vulnerabilities or attack vectors, such as SIM card swapping or sophisticated phishing techniques. However, using 2FA remains one of the most effective methods to protect your online accounts and personal information from unauthorized access.
Here’s a simplified overview of how 2FA works:
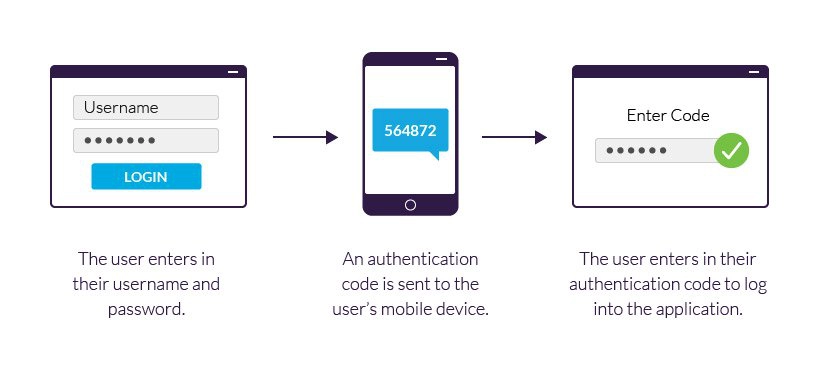
The user initiates login: The user attempts to log in to an account or service by entering their username/email and password.
First-factor authentication (knowledge-based): The system verifies the user’s first factor, which is something they know—their password. If the entered password matches the one stored in the system, the first factor is authenticated.
Second-factor authentication (possession-based): After the first factor is verified, the user is prompted to provide the second factor, which is typically something they have. This could be a verification code sent via SMS, email, or generated by an authenticator app, a physical hardware token, or a biometric scan.
Verification of the second factor: The user enters the verification code, inserts the hardware token, or provides the required biometric data.
Successful authentication: If the second factor is verified successfully, the user is granted access to the account or service. If the second-factor authentication fails, access is denied.
Question: Is it recommended to add 2FA to your bank account? how can you use 2FA for bank account authentification?
Yes, it is highly recommended to enable 2FA for your bank account to enhance its security. Banks are among the primary targets for cybercriminals due to the sensitive financial information they hold, so adding an extra layer of protection is crucial.
Banks typically offer multiple options for implementing 2FA:
SMS or Email Codes: Upon logging in, the bank sends a one-time verification code to your registered mobile number or email address. You enter this code along with your password to complete the authentication process.
Authenticator Apps: Banks may support authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy. After enabling 2FA, you need to scan a QR code provided by the bank using the authenticator app. The app then generates time-based codes that you enter along with your password during login.
Hardware Tokens: Some banks provide physical hardware tokens that generate unique codes for authentication. You would typically need to press a button on the token to display the code and enter it along with your password.
Biometric Authentication: Some banks have integrated biometric authentication methods such as fingerprint or facial recognition. In this case, you would need to authenticate using your biometric data in addition to your password.
The specific methods offered by your bank may vary, so it’s best to check with your bank’s website or contact their customer support for guidance on enabling 2FA for your account. They will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to set it up and use it.
Remember to choose a 2FA method that suits your preferences and offers a good balance between security and convenience. It’s essential to follow best practices such as keeping your mobile device or hardware token secure and ensuring you have backup options in case your primary authentication method is unavailable.
It is important not to disregard two-factor authentication due to the perception that it takes too long to access your account. It is far better to invest a couple of minutes in authenticating your account than to risk losing a significant sum from your bank account or falling victim to hacking, which could compromise your valuable online data.
Ken D